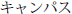Transliterator
Transliterator converts a string between Latin and other scripts. For example:
| Source | Transliteration |
|---|---|
|
|
kyanpasu |
|
Αλφαβητικός Κατάλογος |
Alphabētikós Katálogos |
|
биологическом |
biologichyeskom |
It is important to note that transliteration is not translation. Rather, transliteration is the conversion of letters from one script to another without translating the underlying words.
Note: Standard transliteration methods often do not follow the pronunciation rules of any particular language in the target script.
The Transliterator stage supports the following scripts. In general, the Transliterator
stage follows the UNGEGN Working Group on Romanization Systems guidelines. For more
information, see www.eki.ee/wgrs.
- Arabic
- The script used by several Asian and African languages, including Arabic, Persian, and Urdu.
- Cyrillic
- The script used by Eastern European and Asian languages, including Slavic languages such as Russian. The Transliterator stage generally follows ISO 9 for the base Cyrillic set.
- Greek
- The script used by the Greek language.
- Half width/Full width
- The Transliterator stage can convert between narrow half-width scripts and wider
full-width scripts. For example, this is half-width:
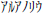 . This is full-width:
. This is full-width: 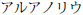 .
. - Hangul
- The script used by the Korean language. The Transliterator stage follows the Korean Ministry of Culture & Tourism Transliteration regulations. For more information, see the website of The National Institute of the Korean Language.
- Katakana
- One of several scripts that can be used to write Japanese. The Transliterator stage uses a
slight variant of the Hepburn system. With Hepburn system, both ZI (
 ) and DI (
) and DI (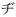 )
are represented by "ji" and both ZU (
)
are represented by "ji" and both ZU (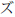 )
and DU (
)
and DU (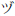 ) are represented by "zu". This is
amended slightly for reversibility by using "dji" for DI and "dzu" for DU.
The Katakana transliteration is reversible.
) are represented by "zu". This is
amended slightly for reversibility by using "dji" for DI and "dzu" for DU.
The Katakana transliteration is reversible. - Latin
- The script used by most languages of Europe, such as English.
Transliterator is part of the Data Normalization Module. For a listing of other stages, see Data Normalization Module.